<< View previous version | view page history | view next version >>
Plugin might have settings, for example, Ant plugin has a setting defining a path to Ant executable. In this tutorial, we will continue to evolve our helloworld plugin to define a message prefix in the plugin setting so that all user specified messages are automatically prefixed with certain string.
First let's define the plugin setting class MyPluginSetting.java:
package com.example.myplugin; import org.hibernate.validator.NotEmpty; import com.pmease.quickbuild.annotation.Editable; // Plugin setting class must contains a default constructor public class MyPluginSetting { private String prefix; @Editable(description="Specify a message prefix here.") @NotEmpty public String getPrefix() { return prefix; } public void setPrefix(String prefix) { this.prefix = prefix; } }
And then tell QuickBuild about this class by modifying MyPlugin.java as below:
... // omitted for brevity public class MyPlugin extends AbstractPlugin { @Override public Object[] getExtensions() { ... // omitted for brevity } @Override public Class<?> getSettingClass() { return MyPluginSetting.class; } }
Finally we modify MyAnotherStep.java to make use of the prefix:
... // omitted for brevity public class MyAnotherStep extends Step { ... // omitted for brevity @Override public void run() { // You may also get the plugin setting object through PluginSettingHelper MyPluginSetting pluginSetting = (MyPluginSetting) getPlugin().getSetting(); Context.getLogger().info(pluginSetting.getPrefix() + ": " + getMessage()); } }
Now start QuickBuild and it prints a warning message complaining that plugin com.example.myplugin needs to be configured. The plugin will temporarily be disabled if stored plugin setting object vilolates constraints of the plugin class. For newly installed plugins, the plugin setting object is initially created by calling default constructor of the plugin setting class.
Gobal plugin setting can be specified by overriding method getPluginSettingClass in the plugin class as follows:
public class MyPlugin extends AbstractPlugin { ... Class<?> getPluginSettingClass() { return MyPluginSetting.class; } ... }
The class MyPluginSetting should be provided by plugin developer, for example:
public class MyPluginSetting { private String property1; private String property2; @Editable(order=100) public String getProperty1 { return property1; } public void setProperty1(String property1) { this.property1 = property1; } @Editable(order=200) public String getProperty2 { return property2; } public void setProperty2(String property2) { this.property2 = property2; } }
With property annotations, QuickBuild will generate the user interface to edit and save setting for this plugin. Refer to [Generate Plugin UI] for details about how to use annotation to define the setting's user interface.
The defined plugin setting object can be retrieved by using following code:
MyPluginSetting myPluginSetting = (MyPluginSetting)PluginSettingHelper.getPluginSetting(MyPlugin.class);
User level plugin setting
User level plugin setting can be specified by overriding method getPluginUserSettingClass in the plugin class. Let's take the MSN Notifier plugin as example:
public class MsnPlugin extends AbstractPlugin { ... Class<?> getPluginUserSettingClass() { Return MsnUserSetting.class; } ... }
And the MsnUserSetting class is defined as follows:
public class MsnUserSetting { private String msnAccount; @Editable(order=100) @Email @NotEmpty public String getMsnAccount() { return msnAccount; } public void setMsnAccount(String msnAccount) { this.msnAccount = msnAccount; } }
This setting adds an attribute "msnAccount" to each user's user interface when a user is edited and displayed:
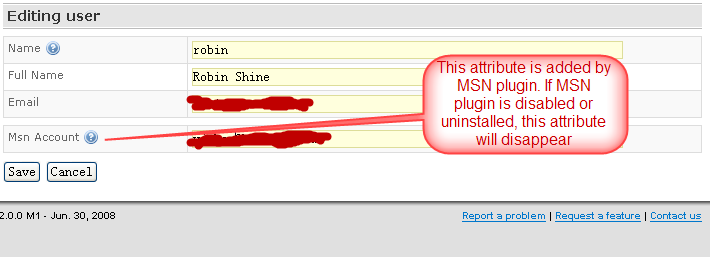
For a particular user, this attribute can be retrieved as follows:
UserSetting userSetting = (UserSetting)PluginSettingHelper.getPluginSetting(MsnPlugin.class, user);
String msnAccount = userSetting.getMsnAccount();
- Group level plugin setting
Group level plugin setting is very similar to user level plugin setting, except that:- Group setting is attached to each group and will be displayed and edited if you view or edit particular group.
- The setting class is specified by overriding method getPluginGroupSettingClass
- The setting object can be retrieved by calling PluginSettingHelper.getPluginSetting(<Plugin Main Class>, <group instance>)
- Configuration level plugin setting
Configuration level plugin setting is very similar to user level plugin setting, except that:- Configuration setting is attached to each configuration and will be displayed and edited if you view or edit particular configuration
- The setting class is specified by overriding method getPluginConfigurationSettingClass
- The setting object can be retrieved by calling PluginSettingHelper.getPluginSetting(<Plugin Main Class>, <configuration instance>)
- Plugin setting migration
Refer to [QBTEAM:Bean Migrator] for how to migrate plugin settings between different plugin versions.